Processes
With increasingly tight tolerance ranges, rectification of steel is becoming increasingly important. It is comparable to bending. Rectification cannot be used to restore the initial state of the workpiece. Various procedures are available.
There are now electromechanical and hydraulically powered rectification benches that operate under computer control. This is particularly advantageous for series production. At Härtha, we use a manual straightening press .
Requirements
The objective behind steel rectification is to ensure compliance with a specified tolerance range for warping. Before, during, and after rectification, the component geometry and the deviations are measured manually or using an NC system. If the shape deviation of series production parts is always the same, a fixed deformation can be set without the need for measurements.
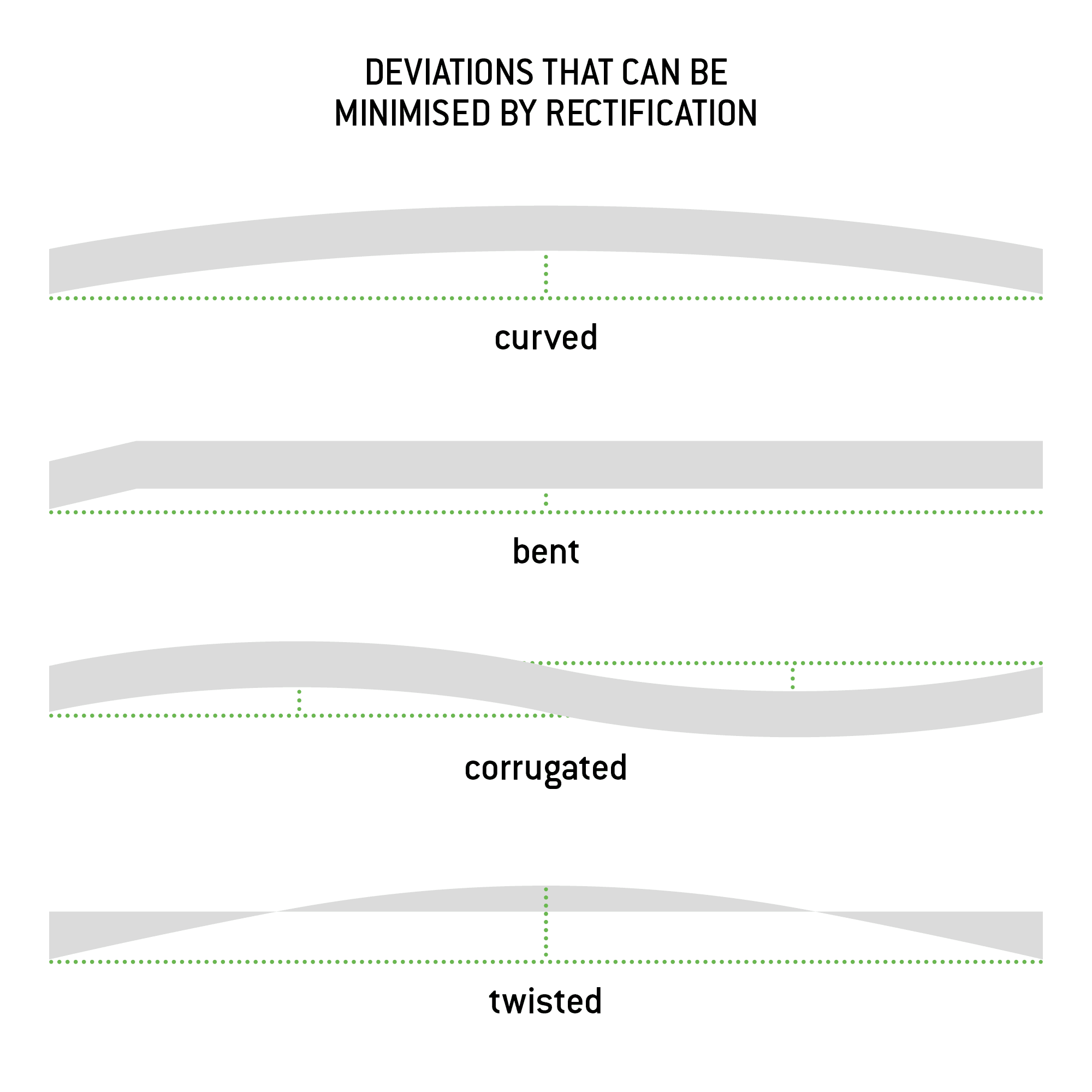
Circular rectification
Circular rectification refers to various methods for rectifying round components. Deviations are measured by means of sensors during rotation. It is important that these sensors make contact with the component throughout the measurement. Circular rectification is differentiated into rolling rectification and bending rectification.
Rolling rectification
Rolling rectification is most commonly used early in the manufacturing process of components, for example for blanks after forging. It is intended to achieve flatness in the material and reduce tensions. This type of circular rectification usually impacts the entire component.
Bending rectification
Bending rectification is intended to eliminate existing deviations by means of a targeted correction. This requires measurement of the component’s geometry and of concentricity deviations. Only then can the workpiece be correctly positioned in the rectification press.
Next, the bending stroke is performed by the press. This can be done manually or using an NC system.
High-frequency hammering
High-frequency hammering is suitable, for example, for welds or for increasing the service life of components. This rectification method makes it possible to treat deformations and residual stresses in specific areas of the component. Particularly high dimensional stability can be achieved.
Moulding rectification
Moulding rectification is suitable for components that are not rotationally symmetrical, such as aluminium castings. This requires that the measuring device is calibrated to a target value. Rectification is performed by bending.
INFO: Rectification of pipes
The production of pipes often brings about straightness deviations which need to be rectified. In the past, the straightness of pipes was determined subjectively by visual judgement. Today, pipes often need to meet highly specific requirements. For example, a 1-metre pipe must have a straightness deviation no greater than 0.2 mm. The permissible deviations increase accordingly with the length of the pipes. These stringent requirements require the use of state-of-the-art rectification machines.
Applications
Rectification can be applied wherever warping occurs on steel parts – whether during thermal or mechanical metalworking. Warping can also occur during the use of workpieces. Rectification is suitable for all types of steel - from non-alloy construction steel to quenched and tempered special steel.
Advantages
Depending on the procedure, rectification offers the following advantages:
- Great dimensional stability
- Optimum flatness
- Suitable for different component geometries
- Suitable for different types of steel
Customer information
Would you like to commission our services for rectifying your workpieces made of steel, stainless steel or aluminium? Then we will first need the following information about your workpiece:
- Material designation
- Hardness
- Heat treatments
- Weight and quantity
- Dimensions
Process locations
Refer to our location overview to find the Härtha location closest to you, and to learn which processes we offer besides the rectification of steel.