The process and its advantages
During carbonitriding, the steel component is heated in a gas mixture composed of 0.5% to 0.8% carbon and 0.2% to 0.4% nitrogen. This causes the carbon and nitrogen to diffuse into the steel surface. The component is afterwards quenched in water, oil, or a salt melt. The process concludes by tempering the component at 160 °C to 300 °C in order to reduce brittleness.
Compared to carburising, carbonitriding requires lower temperatures, between 820 °C and 900 °C, and is also generally shorter. These are ideal prerequisites for minimum warping. What is more, the nitrogen lowers the cooling rate that is critical for the formation of martensite, resulting in improved hardenability.
The hardness penetration depth depends on the general hardenability of the steel grade, the component geometry, the carbonitrided layer, the hardening temperature, and the cooling rate. The maximum hardness penetration that can be achieved with carbonitriding is 1.0 mm.
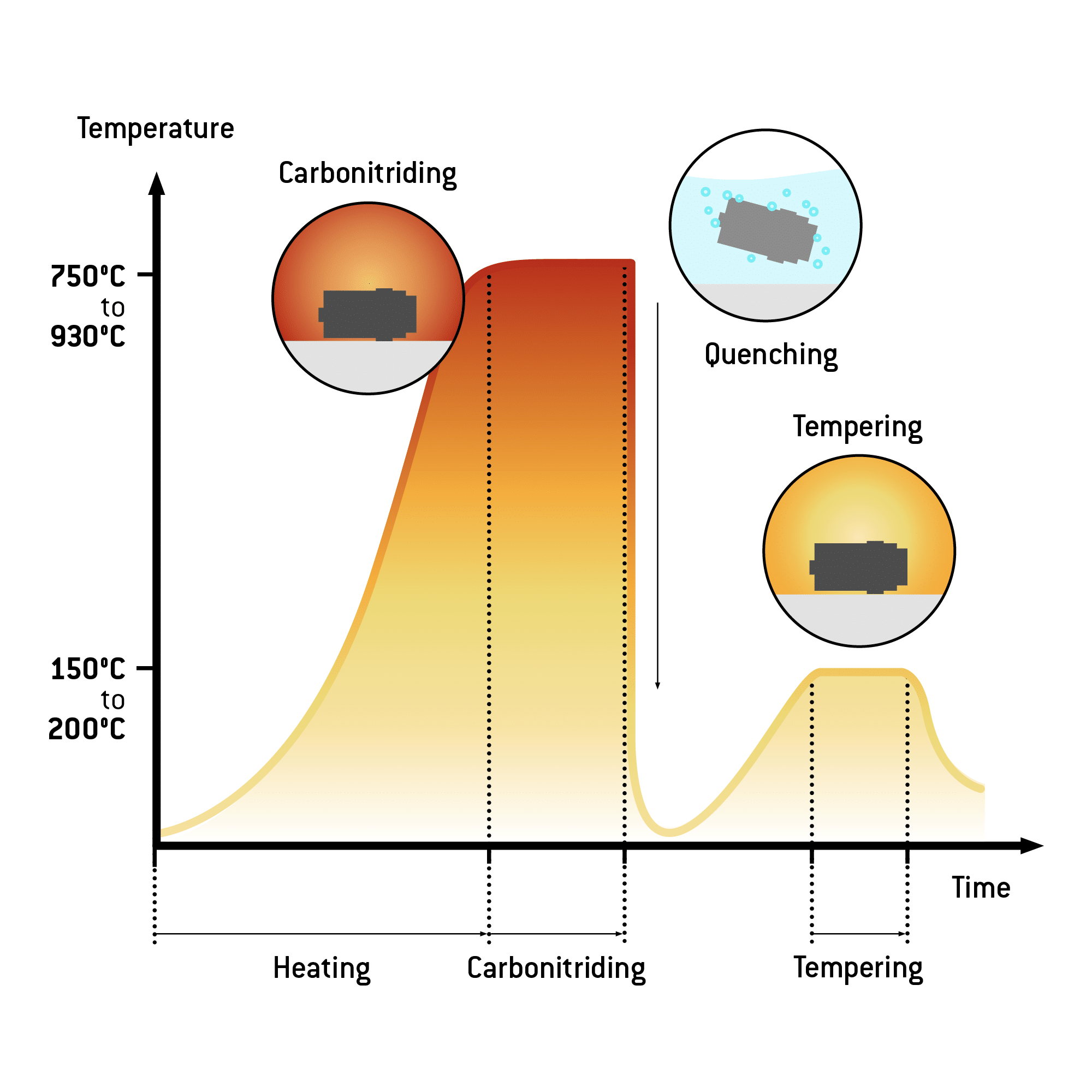 Steps of the carbonitriding process
Steps of the carbonitriding process
Categorisation of carbonitriding heat treatment
Despite the name of the process, carbonitriding is not a nitriding process. Instead, carbonitriding is a hardening process. This is due to the low amount of nitrogen absorbed into the microstructure. The result is that no compound layer forms during heating. In fact, the hard edge layer forms during the quenching process.
The advantages at a glance
Carbonitriding offers many advantages for the treated components:
- The hardenability of alloy and non-alloy steels is increased by the enrichment with nitrogen and carbon.
- The edge layer becomes harder and more wear-resistant than that produced by case hardening.
- Only slight warping thanks to lower temperatures compared to case hardening.
- No cracks, thanks to milder quenching media.
- Improved emergency running properties and better friction wear resistance
- Greater tempering resistance as a function of the nitrogen diffused into the edge layer.
- Ideal for the series production of small components that require a clean environment.
the process and its advantages
Carbonitriding is used to increase the fatigue strength and wear resistance of various grades of steel. The process is of particular interest for components whose case hardening depth is intended to range between 0.1 mm and 1.00 mm. It is very suitable for mass production and for small workpieces.
Examples of components typically treated by carbonitriding include pistons, rollers, shafts, gear wheels, and levers for various types of drive mechanisms.
Suitable materials
Carbonitriding is suitable exclusively for steels with a maximum carbon content of 0.25%. Primarily, these are non-alloy and low-alloy case-hardened steels, as well as sintered, construction, and machining steels.
In our material table you can see an excerpt of suitable materials.
Customer specifications for the heat treatment
Would you like us to perform carbonitriding for you? To complete your order, we need the following information:
- Type of material
- Desired case hardening depth
- Target edge hardness
- Where relevant, the insulation requirements
We will firstly advise you whether the desired hardness values can be realised for your type of material. Afterwards, you will receive our ordering form including all other necessary information.
Process locations
Refer to our location overview to learn which Härtha locations offer carbonitriding.